Date:Mon 8/12/2024 1:00 PM
Happy Monday everyone! Today's fish of the day is the Giant isopod!
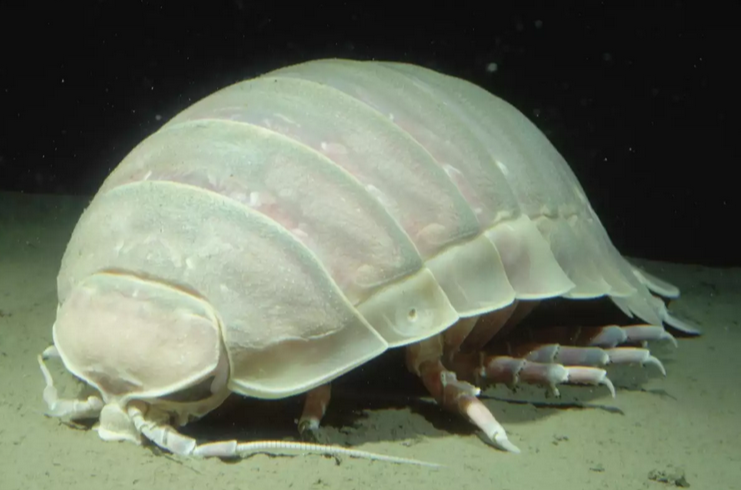

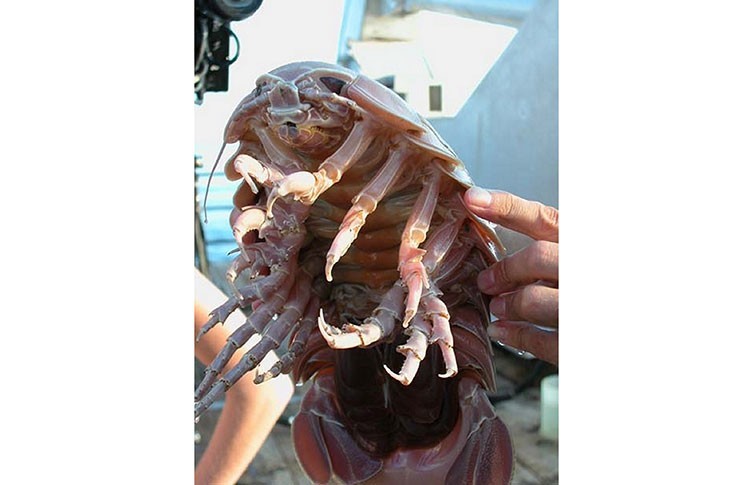
The giant isopod, describes around 20 species in the Bathynomus genus, but most information is based on the Bathynomus giganteus, which is known for being the first giant isopod discovered, and the largest. Giant isopods, as an arthropod, have seven pairs of legs, four jaws, and compound eyes that have over 4,000 facets. The first set of legs is modified into an appendage for grabbing food and bringing it into the mouth, along with attacking prey, and all species with the Bathynomus genus are similar, showing a lack of evolution between populations The full range of this family is unknown, but they can be found around the Indo-Pacific and the Eastern Atlantic ocean. The first time a giant isopod was found and recorded was in 1879 in the Gulf of Mexico, where the largest populations of giant isopods live, with a depth range of 310-2140 meters of depth. Outside of the Gulf of Mexico the other populations have a near identical depth range, and due to their similarity to their close land dwelling cousins, rolly pollies or woodlouse as you might know them, they are one of the textbook examples of deep sea gigantism.
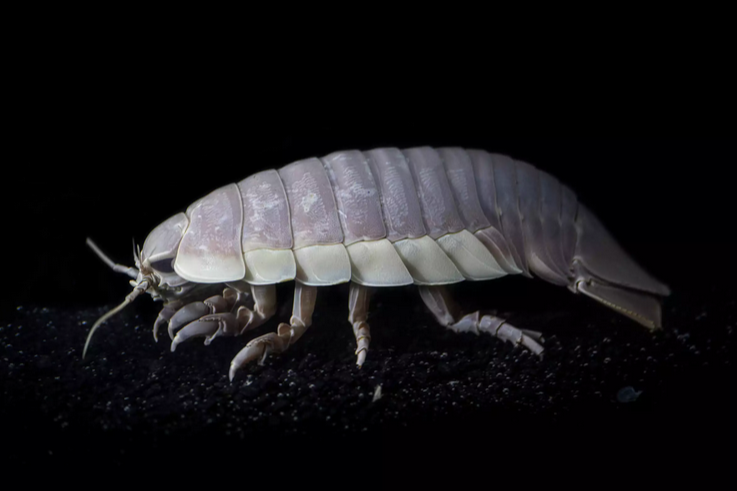

Deep sea gigantism is an observed phenomena where deep sea animals have a habit of getting far larger than their more shallow relatives. Examples of this would be the giant squid, giant sea spider, deepwater stingrays, the bigfin squid,oarfish, and many more. There is currently no encompassing explanation for why this phenomena is so prevalent, but there are multiple theories that have been proven partially correct by different genus. Food scarcity is often referenced, and often thought to be the reason for the giant isopods' large size. as without much food in the deep ocean organisms with the ability to store more food can live for longer periods without prey. Another explanation is the increase in dissolved oxygen, which is often a limiting factor in how large animals can become in their environments. A study of amphipod crustaceans in 1999 discovered their increase in size as the populations found in deeper waters directly increased with the amount of dissolved oxygen. The last and often most damning explanation for deep sea gigantism is the lowered temperature in deeper waters. This one can increase the size in animals by increasing cell size and lifespan, something that can also be found at the world's poles. Deep sea gigantism allows for the giant isopod to get anywhere between 19-36cm (7.5-14.3 inches) in length, with the largest recorded being 20 inches, about the size of a small dog. As compared to their close land relatives, which come in at less than an inch of length.
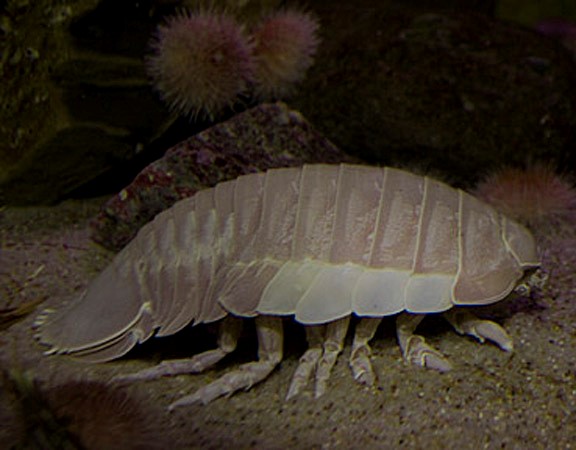

The diet of the deep sea isopod is remarkably similar to that of the land dwelling isopods, as the land dwelling isopods live off of dead or decomposing animals or plant materials. Which is similar to the diet of the giant isopod, which is an essential scavenger and carnivore in the deep. Once believed to be only scavengers, it is now known that giant isopods also actively pursue prey, usually fish, squid, shrimp, crabs, and other deep sea animals they can catch, as shown by a video of an isopod grabbing a dogfish shark and eating its face. These isopods can take down prey several times larger than them, but this may be only when in a confined space, as they don't swim fast and can only attack prey they can catch. But, as scavengers in the deep the giant isopod is primarily known for eating from whalefalls. A whalefall being when the carcass of a dead whale drifts to the deep seafloor, creating huge ecosystem hotspots and specialized animals in deep waters that feed almost exclusively on them. After eating from these whalefalls, giant isopods have been shown to go as long as 5 years in captivity without eating again, and for this reason when in the presence of food they eat far more than their body weight or size, willing to sacrifice locomotion in favor of excess, an easy trade considering they have no natural predators. Despite having no predators, they still have several behaviors similar to land pill bugs, as they can still roll into a ball shape, using their chitin armor to protect themselves, and burrow into the sediment to semi-hibernate.
The reproduction of the giant deep sea isopod is like that of many other arthropods, relying on eggs. In the spring and winter months the isopod females will begin brooding eggs, this is done in a pouch above the stomach and it will store anywhere between 20-30 eggs. During the brooding the female will burrow down into the sediment and refuses to leave until all eggs are hatched, at which point the juveniles are left. Captive isopods eggs measure 13mm in diameter and are thought to possibly be the largest marine invertebrate egg. Once born, these juvenile giant isopods will be as large as 4 inches in length ,and set off on their own in a stage called manca. At this stage, these are almost fully developed giant isopods, lacking only the last pair of legs. These will grow over time, and these animals gain size through molts. Their full lifespan is unknown, but estimated to be decades long, with the age of sexual maturity being unknown but estimated anywhere from 15-18 months.
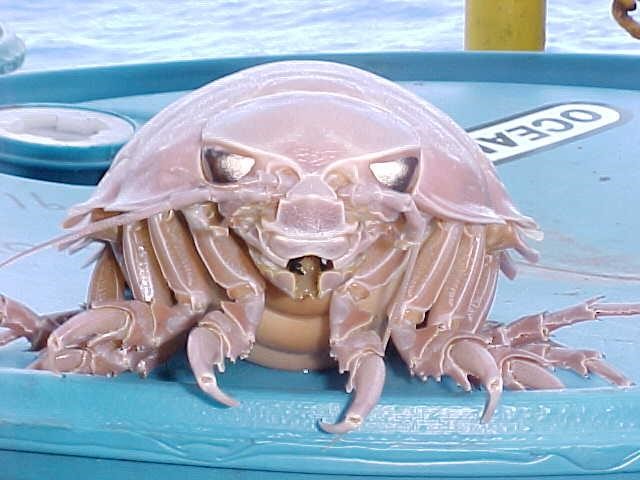

That's the giant isopod everybody! Have a wonderful Monday, and a great week ahead!